When working with complex systems such as those utilizing Lua scripting within the Path of Building tool, users can encounter a variety of errors that can cause frustration and slow down their workflow. This article aims to clarify common Lua errors that users may encounter while using Path of Building, as well as to provide solutions to resolve these issues. In addition, we will discuss best practices for securely using AI technologies in business environments, focusing on tools like the Adastra LLM Gateway and the importance of data encryption.
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Common Lua Errors in Path of Building
- 2.1 Syntax Errors
- 2.2 Runtime Errors
- 2.3 Logic Errors
- Fixing Common Lua Errors
- 3.1 Debugging Syntax Errors
- 3.2 Runtime Error Solutions
- 3.3 Addressing Logic Errors
- Best Practices for Secure AI Usage
- 4.1 Importance of Data Encryption
- 4.2 Implementing API Gateways like Adastra LLM Gateway
- Conclusion
- Code Example
- Resources
1. Introduction
In the age of digital transformation, using tools like Path of Building, which relies on Lua scripting for enhanced functionality, has become increasingly popular among users who want to optimize their performance in various applications. However, working with Lua can lead to specific errors that hinder productivity. Understanding these common errors will not only facilitate quicker resolutions but will also automate better practices when dealing with AI.
APIPark is a high-performance AI gateway that allows you to securely access the most comprehensive LLM APIs globally on the APIPark platform, including OpenAI, Anthropic, Mistral, Llama2, Google Gemini, and more.Try APIPark now! 👇👇👇
2. Common Lua Errors in Path of Building
Lua scripting can result in various issues, primarily categorized into three types: syntax errors, runtime errors, and logic errors. Below, we’ll define each type of error to provide clarity.
2.1 Syntax Errors
Syntax errors occur when the code does not follow the proper language rules. Common examples include:
– Missing brackets
– Incorrect use of indentation
– Misspelled commands
– Unmatched quotation marks
Example Syntax Error:
print("Hello World" -- Missed closing parenthesis
2.2 Runtime Errors
Runtime errors arise when the code is syntactically correct but fails when executed. Examples include:
– Accessing null or undeclared variables
– Indexing a table with a nil value
– Calling a function that is not defined
Example Runtime Error:
print(myVariable) -- myVariable is not defined
2.3 Logic Errors
Logic errors occur when the code does not perform as intended despite being free of syntax and runtime errors. These errors can be challenging to detect, as the code runs without throwing exceptions, leading to incorrect results.
Example Logic Error:
if x = 10 then -- Should be '==' for comparison
print("X is ten")
end
3. Fixing Common Lua Errors
In the section that follows, we will discuss how to diagnose and fix common Lua errors that users encounter while using Path of Building.
3.1 Debugging Syntax Errors
When you suspect a syntax error, here are steps to identify and fix it:
– Use a Lua editor with real-time syntax highlighting that will flag errors as they occur.
– Check for mismatched parentheses and punctuation.
– Comment out sections of code to isolate problematic areas.
3.2 Runtime Error Solutions
To resolve runtime errors:
– Make sure to define all your variables before using them. It’s beneficial to initialize variables explicitly.
– Use print statements to log variable values leading up to the error.
Fixing Example Runtime Error:
local myVariable = "Defined"
print(myVariable) -- Correctly defined
3.3 Addressing Logic Errors
Logic errors require careful examination of the code.
– Use debugging tools to follow the flow of execution and inspect variable values at each step.
– Ensure that all conditional checks are correctly formed.
4. Best Practices for Secure AI Usage
As businesses increasingly adopt AI technologies, security becomes paramount. Using solutions like the Adastra LLM Gateway can streamline API calls while enhancing security.
4.1 Importance of Data Encryption
Incorporating data encryption measures ensures that sensitive information remains protected during transmission and storage. Organizations must prioritize encryption to mitigate risks associated with data breaches.
| Data Security Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Encryption | Scrambling data to prevent unauthorized access |
| API Token Security | Using unique tokens for API access control |
| Role-Based Access | Limiting access based on user roles |
4.2 Implementing API Gateways like Adastra LLM Gateway
Utilizing an API gateway can greatly enhance your organization’s security and efficiency when interacting with AI services. The Adastra LLM Gateway provides independent management of API requests, ensuring data integrity and governance.
5. Conclusion
Understanding Path of Building Lua errors and how to fix them enhances user productivity and ensures smoother workflows. By adopting security best practices, including data encryption and effective API gateways, organizations can confidently leverage AI technologies.
6. Code Example
Here’s an example of a properly formatted Lua script for Path of Building, including error handling:
local function greetUser(name)
if name == nil then
print("Error: Name cannot be nil")
else
print("Hello, " .. name .. "!")
end
end
greetUser("Alice") -- Proper usage
greetUser(nil) -- Will trigger error message
7. Resources
For more information on Path of Building, Lua scripting, and secure AI practices, consider checking the official documentation and current best practices:
By thoroughly understanding and addressing Path of Building Lua errors, combined with practicing proper security measures, organizations can significantly improve their operational efficiency while securely managing AI capabilities.
This article provides a structured approach to understanding and resolving Lua errors within the Path of Building context, while also emphasizing the significance of maintaining secure practices in AI deployments.
🚀You can securely and efficiently call the The Dark Side of the Moon API on APIPark in just two steps:
Step 1: Deploy the APIPark AI gateway in 5 minutes.
APIPark is developed based on Golang, offering strong product performance and low development and maintenance costs. You can deploy APIPark with a single command line.
curl -sSO https://download.apipark.com/install/quick-start.sh; bash quick-start.sh
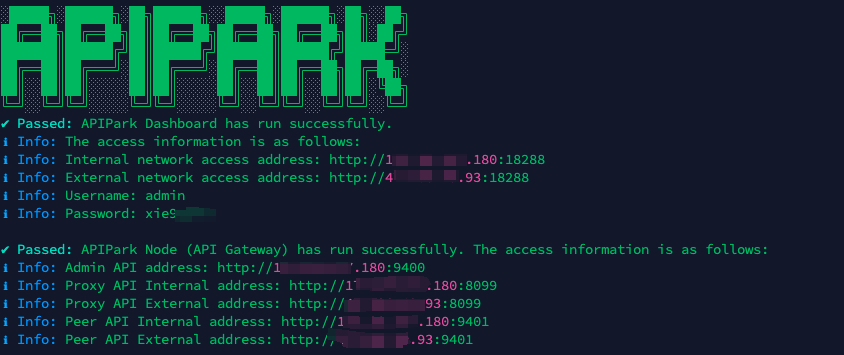
In my experience, you can see the successful deployment interface within 5 to 10 minutes. Then, you can log in to APIPark using your account.
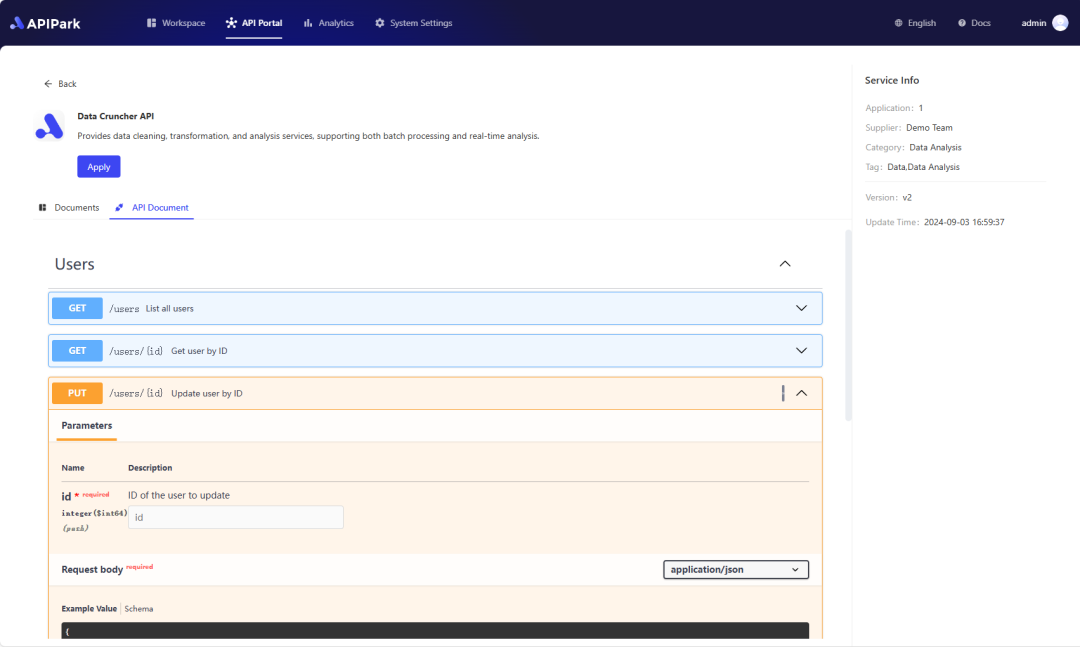
Step 2: Call the The Dark Side of the Moon API.