In today’s fast-paced digital environment, selecting the right operational paradigm for your applications is crucial. The decision between caching and stateless operations can significantly impact performance, scalability, and security. This article delves into the nuances of these two methodologies, helping you make informed choices for your enterprise’s needs.
Introduction to Caching and Stateless Operations
Before diving into comparisons, it’s essential to understand what caching and stateless operations entail. Both approaches are designed to optimize performance but do so in fundamentally different ways.
Caching
Caching involves storing copies of data in a temporary storage location to reduce retrieval times. By keeping frequently accessed data closer to the processor, caching minimizes the need to repeatedly fetch the same data from slower storage locations. This can lead to significant performance improvements, especially in scenarios requiring repeated access to the same information.
Stateless Operations
Stateless operations, on the other hand, treat each request independently. Each operation is self-contained, with no reliance on previous interactions. This approach is particularly beneficial in distributed systems, where maintaining state across multiple nodes can be challenging. Stateless operations often lead to simpler, more scalable applications.
Key Differences Between Caching and Stateless Operations
To better understand which approach suits your application, let’s compare their key characteristics:
| Feature | Caching | Stateless Operations |
|---|---|---|
| State Management | Maintains state information in cache | No state information maintained |
| Performance Impact | Reduces data retrieval times | Simpler logic, potentially more CPU usage |
| Scalability | Can be complex due to state synchronization | Highly scalable due to lack of state |
| Complexity | May require sophisticated cache management | Typically simpler and more straightforward |
| Fault Tolerance | Can be prone to cache invalidation issues | More resilient to node failures |
Caching in Practice
Caching is a powerful technique that can dramatically enhance application performance. However, it requires careful management to avoid issues like data staleness and cache thrashing. Let’s explore how caching can be implemented effectively in a web application.
Implementing Caching with Træfik
Træfik is a popular open-source edge router that provides a range of features, including load balancing, HTTPS termination, and caching capabilities. Here’s a basic example of configuring caching in Træfik:
http:
middlewares:
my-cache:
cache:
ttl: 10m
stale: 5m
routers:
my-api:
rule: "Host(`api.example.com`)"
service: my-service
middlewares:
- my-cache
In this YAML configuration, a middleware named my-cache is set up with a time-to-live (TTL) of 10 minutes and a stale period of 5 minutes. This configuration helps ensure that frequently accessed API responses are cached, reducing load times and server strain.
Stateless Operations in Practice
Stateless operations offer a different set of advantages. By eliminating dependencies on stored state, applications can achieve greater resilience and scalability. Let’s look at how stateless design is applied in API development.
Designing Stateless APIs
An API designed with stateless principles treats each request independently. This means that all necessary data must be included in each request, often through query parameters or headers. Here’s an example of a stateless API endpoint:
GET /user/profile?userId=12345 HTTP/1.1
Host: api.example.com
Authorization: Bearer <token>
In this request, all the information needed to fetch the user profile is included in the request itself. The server does not retain any session data between requests, making it easier to manage and scale.
APIPark is a high-performance AI gateway that allows you to securely access the most comprehensive LLM APIs globally on the APIPark platform, including OpenAI, Anthropic, Mistral, Llama2, Google Gemini, and more.Try APIPark now! 👇👇👇
Enterprise Security and AI
As enterprises increasingly integrate AI into their operations, understanding the implications for security becomes vital. AI can offer significant benefits, but it also introduces new challenges.
Safe AI Practices in Enterprises
- Data Privacy: Ensure that AI systems comply with data protection regulations and that sensitive information is adequately anonymized.
- Model Security: Protect AI models from threats like adversarial attacks or data poisoning.
- Access Controls: Implement robust access controls to prevent unauthorized use of AI systems.
Leveraging AI with Træfik
Træfik can be integrated with AI-driven solutions to enhance routing capabilities. For instance, AI algorithms can be used to dynamically adjust routing rules based on traffic patterns, improving efficiency and resource utilization.
Routing and Rewrite Rules
Effective API management often involves routing and rewriting rules to direct traffic appropriately and ensure seamless user experiences.
Utilizing Routing Rewrite in Træfik
Routing rewrites allow for dynamic URL adjustments, enabling flexible and efficient traffic management. Here’s an example of a rewrite rule in Træfik:
http:
middlewares:
redirect:
redirectRegex:
regex: "^http://(.*)"
replacement: "https://$1"
permanent: true
routers:
my-router:
rule: "Host(`example.com`)"
service: my-service
middlewares:
- redirect
In this setup, all incoming HTTP requests are redirected to HTTPS, enhancing security and ensuring consistent access.
Conclusion
Choosing between caching and stateless operations largely depends on your application’s specific needs. Caching can offer substantial performance improvements but requires careful management to avoid complexity and staleness issues. Stateless operations, while simpler and more scalable, may involve higher computational costs.
Ultimately, the right choice depends on factors such as application architecture, performance requirements, and operational scale. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each approach, you can make informed decisions that align with your enterprise’s goals and ensure robust, efficient, and secure application management.
🚀You can securely and efficiently call the 文心一言 API on APIPark in just two steps:
Step 1: Deploy the APIPark AI gateway in 5 minutes.
APIPark is developed based on Golang, offering strong product performance and low development and maintenance costs. You can deploy APIPark with a single command line.
curl -sSO https://download.apipark.com/install/quick-start.sh; bash quick-start.sh
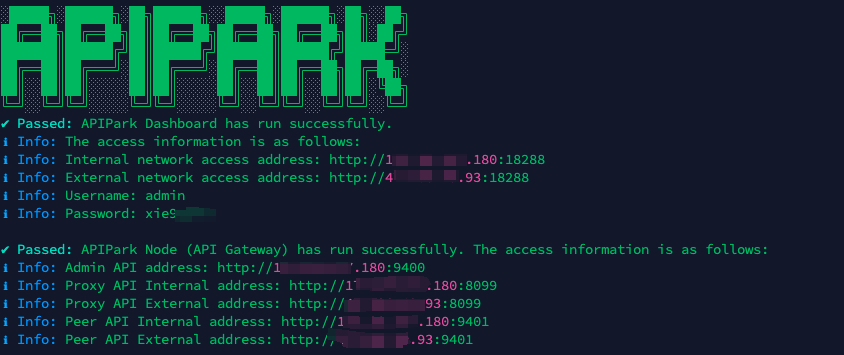
In my experience, you can see the successful deployment interface within 5 to 10 minutes. Then, you can log in to APIPark using your account.
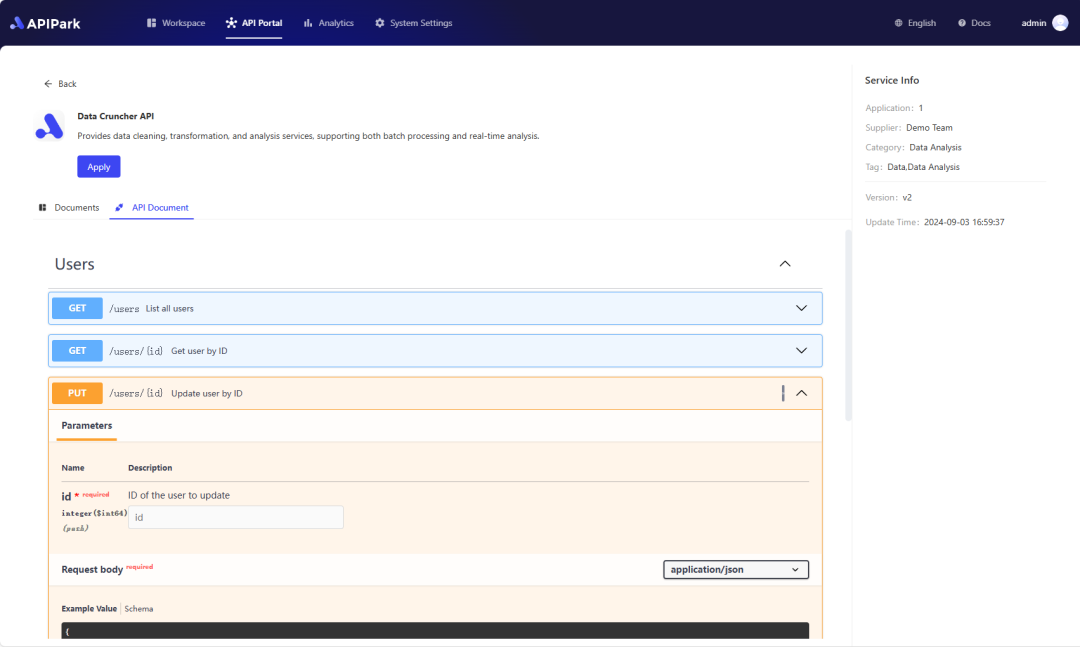
Step 2: Call the 文心一言 API.