Helm is one of the most popular package managers for Kubernetes. With its rich set of features, it simplifies the process of deploying applications and services on a Kubernetes cluster. As developers or DevOps teams engage with Helm, one common task they encounter is accessing arguments passed during the helm upgrade command. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide on how to access these arguments effectively. Additionally, we’ll explore how services like APIPark, IBM API Connect, and the API Developer Portal enhance API management, along with real-time statistics that help in understanding API performance.
Understanding helm upgrade
The helm upgrade command is used to upgrade a release to a new version of a chart. One of the most powerful features of this command is the ability to pass custom values that can modify the behavior or configuration of your application. For instance, if you wanted to change an environment variable or adjust resource limits, you could pass these values directly through the command line.
The Command Structure
A common structure of the helm upgrade command is:
helm upgrade [RELEASE] [CHART] [flags]
Here, [RELEASE] denotes the name of your release, [CHART] is the location of the chart, and [flags] can include various options like --set or -f for specifying value files.
Example Command
helm upgrade my-release my-chart --set image.tag=2.0.0 --namespace my-namespace
In this example, we’re upgrading my-release to use the my-chart chart and changing the image.tag value to 2.0.0 in the namespace my-namespace.
Accessing Arguments Passed to helm upgrade
When you pass arguments to helm upgrade, they can be accessed within your Kubernetes deployments or configurations using the Helm templating system. Here’s how to do it step by step:
Step 1: Setting Up the Chart Template
Assuming you have a Helm chart set up, navigate to the templates directory. You can modify the Deployment.yaml file to access the values you passed in via the helm upgrade command.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: {{ .Release.Name }}
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: {{ .Release.Name }}
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: {{ .Release.Name }}
spec:
containers:
- name: my-container
image: "myimage:{{ .Values.image.tag }}"
In the example above, {{ .Values.image.tag }} allows you to access the image.tag value passed during the helm upgrade.
Step 2: Using the Values in Configuration
To ensure that values are applied as expected, you can define defaults in the values.yaml file of your Helm chart:
image:
repository: myimage
tag: 1.0.0
This will ensure that if no other value is provided during the upgrade, Helm defaults to using 1.0.0.
Step 3: Checking the Installed Release for Values
Once the Helm upgrade is successfully executed, you can verify that your application is running with the new configuration. Use the following command to get the details:
helm get values my-release
This command outputs the values in use for the specified release, allowing you to confirm what you passed in.
Step 4: Debugging
If you run into issues, the --debug flag can provide more context about what Helm is doing behind the scenes:
helm upgrade my-release my-chart --set image.tag=2.0.0 --namespace my-namespace --debug
Using APIPark with Helm Upgrades
As you explore how to utilize Helm effectively, tools like APIPark can streamline your API management process. APIPark serves as an asset management platform, making it easier for developers to engage with APIs post-deployment.
Features of APIPark
APIPark provides:
- Centralized API Management: Easily manage and showcase all your APIs.
- Lifecycle Management: Automate various API operations, ensuring high-quality service throughout their lifecycle.
- Multi-Tenant Support: Facilitates independent management of different user resources, improving data security and efficiency.
- Logging and Statistics: Detailed logs and performance metrics provide crucial insights into API usage.
These features complement Kubernetes and Helm by ensuring your deployed services are robust, monitored, and easily accessible.
Table of Key APIPark Components
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Centralized Management | Provides a unified view of APIs across teams |
| Lifecycle Management | Supports full API lifecycle from design to retirement |
| Multi-Tenant Architecture | Isolates resources and permissions for different users |
| Real-Time Statistics | Offers insights into API performance and usage trends |
Integrating with IBM API Connect
Moreover, integrating with IBM API Connect can further enhance your API management capabilities. It provides robust features such as security, analytics, and monitoring, which work synergistically with Helm deployment strategies.
API Runtime Statistics
The integration enables businesses to track API Runtime Statistics, allowing them to analyze usage patterns, detect anomalies, and optimize performance based on real-time data feedback.
Conclusion
In conclusion, accessing arguments passed during the helm upgrade process can be straightforward when properly understood and implemented. Leveraging the power of Helm alongside API management solutions like APIPark and IBM API Connect creates a comprehensive development environment. With clear processes in place and effective tools at your disposal, modern software deployment and API management can be both efficient and effective.
Whether managing complex upgrades in Kubernetes or ensuring smooth API operations, understanding the nuances of Helm and combining it with powerful API management features is crucial to achieving scalable and maintainable applications.
APIPark is a high-performance AI gateway that allows you to securely access the most comprehensive LLM APIs globally on the APIPark platform, including OpenAI, Anthropic, Mistral, Llama2, Google Gemini, and more.Try APIPark now! 👇👇👇
Sample Code
Here’s an example code snippet for creating a simple deployment with Helm, detailing how you can use values dynamically:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: {{ .Release.Name }}
labels:
app: {{ .Release.Name }}
spec:
replicas: {{ .Values.replicaCount }}
selector:
matchLabels:
app: {{ .Release.Name }}
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: {{ .Release.Name }}
spec:
containers:
- name: my-app
image: "{{ .Values.image.repository }}:{{ .Values.image.tag }}"
ports:
- containerPort: {{ .Values.service.port }}
This adoption of Helm, along with integrated management solutions like APIPark, can vastly enhance the way teams handle service upgrades—providing a more robust and dynamic development lifecycle. By combining Kubernetes’ capabilities with effective API management, organizations can ensure their services run smoothly and efficiently in a competitive environment.
🚀You can securely and efficiently call the The Dark Side of the Moon API on APIPark in just two steps:
Step 1: Deploy the APIPark AI gateway in 5 minutes.
APIPark is developed based on Golang, offering strong product performance and low development and maintenance costs. You can deploy APIPark with a single command line.
curl -sSO https://download.apipark.com/install/quick-start.sh; bash quick-start.sh
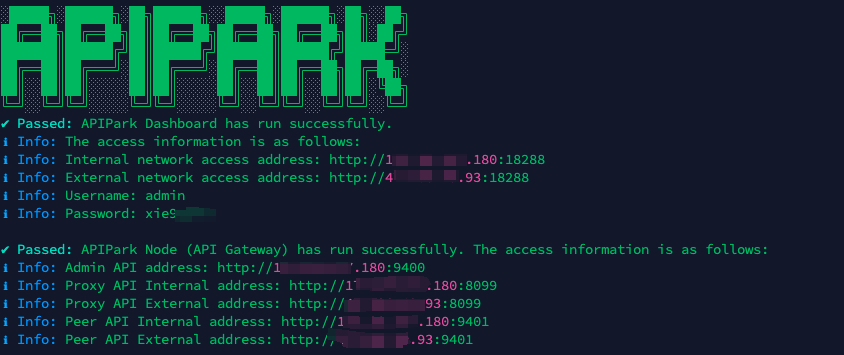
In my experience, you can see the successful deployment interface within 5 to 10 minutes. Then, you can log in to APIPark using your account.
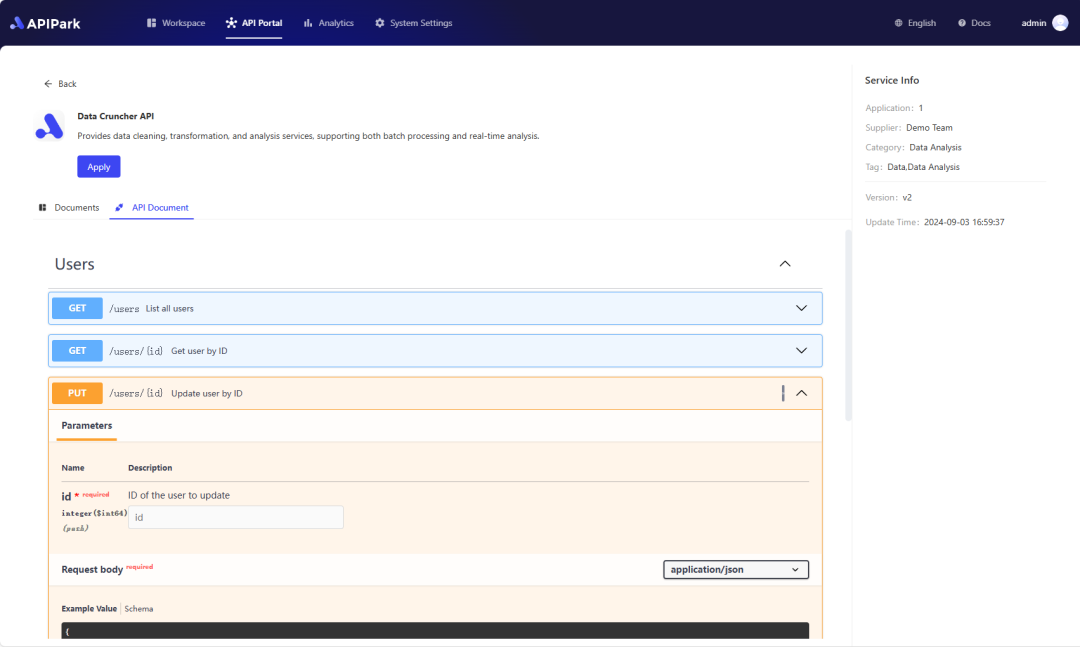
Step 2: Call the The Dark Side of the Moon API.