Building microservices can be an exciting journey, especially for those looking to develop scalable and efficient applications. This guide will lead you step-by-step through the process, while incorporating essential components such as AI security, nginx, Open Platform, and IP Blacklist/Whitelist. Let’s get started!
Understanding Microservices
Before diving into the process of building microservices, it’s crucial to understand what they entail. Microservices is an architectural style that structures an application as a collection of loosely coupled services. This means that each service corresponds to a specific business function and can be developed and deployed independently.
Key Characteristics of Microservices
- Scalability: Each microservice can be scaled independently based on demand.
- Flexibility: Each service can use different technologies and programming languages.
- Resilience: If one microservice fails, it doesn’t necessarily bring down the entire application.
- Ease of Deployment: Microservices can be deployed quickly, making it easier to roll out new features or fixes.
Step 1: Plan Your Microservices Architecture
The first step in building microservices is to design your architecture. This involves defining the services that your application requires and how they will interact. Here are several tips to consider:
- Identify Business Capabilities: Start by identifying the core functionalities of your application.
- Decouple Services: Each service should be independent enough to allow for changes without affecting others.
- Define API Contracts: Develop clear contracts for how your services will communicate with each other.
Example of Microservices Architecture
Below is a simple example of a microservices architecture for an e-commerce application:
| Service Name | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| User Service | Manages user accounts and profiles |
| Product Service | Handles product inventory and details |
| Order Service | Processes user orders |
| Payment Service | Manages payment processing |
Step 2: Choose the Technology Stack
Choosing the right technology stack is vital for your microservices architecture. Here are some popular technologies:
- Language: Java, Node.js, Python, Go
- Database: MongoDB, PostgreSQL, MySQL
- API Gateway: NGINX, Kong, Zuul
- Containerization: Docker, Kubernetes
For beginners, using a simple API gateway like NGINX can help manage requests more efficiently and provide load balancing.
NGINX Configuration Example
Here’s a basic configuration to set up NGINX for your microservices:
http {
server {
listen 80;
location /user {
proxy_pass http://user_service:8080;
}
location /product {
proxy_pass http://product_service:8081;
}
location /order {
proxy_pass http://order_service:8082;
}
}
}
Step 3: Implement API Security
When building microservices, AI security is crucial for protecting your services from threats. Implement the following security measures:
- Authentication: Ensure that only authorized users can access your microservices.
- Rate Limiting: Protect your services from being overwhelmed by too many requests.
- IP Blacklist/Whitelist: Control which IP addresses can access your services by maintaining a blacklist of malicious IP addresses and a whitelist of trusted IPs.
Setting up IP Blacklist/Whitelist in NGINX
You can easily configure NGINX to allow only specific IP addresses:
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
server {
listen 80;
location / {
allow 192.168.1.1; # allow specific IP
deny all; # deny others
}
}
}
Step 4: Deploy Your Microservices
Once you’ve built your microservices, it’s time to deploy them. Here are some steps you can follow:
- Containerization: Use Docker to containerize each microservice, making it easier to deploy and manage.
- Orchestration: Use Kubernetes or Docker Swarm for orchestration, enabling easy scaling and management of containerized applications.
- Monitoring: Implement monitoring tools to keep track of the health and performance of your microservices.
Example Dockerfile
Here’s a simple Dockerfile for a Node.js microservice:
# Dockerfile
FROM node:14
WORKDIR /usr/src/app
COPY package*.json ./
RUN npm install
COPY . .
EXPOSE 8080
CMD ["node", "app.js"]
APIPark is a high-performance AI gateway that allows you to securely access the most comprehensive LLM APIs globally on the APIPark platform, including OpenAI, Anthropic, Mistral, Llama2, Google Gemini, and more.Try APIPark now! 👇👇👇
Step 5: Test Your Microservices
Testing is a critical step in ensuring your microservices function as expected. Here are some types of tests you should consider:
- Unit Testing: Test individual components of your services.
- Integration Testing: Ensure that different microservices can communicate effectively.
- End-to-End Testing: Simulate real user scenarios to validate functionality.
Step 6: Iterate and Enhance
Microservices development is an ongoing process. Once deployed, you will likely need to enhance and refine your services. Regular updates and improvements are essential to keep your services relevant and secure.
Conclusion
Building microservices may seem daunting, especially for beginners. However, by following this step-by-step guide, you can create a robust and scalable microservices architecture. Remember to prioritize security, scalability, and collaboration among your services. With continuous training, iteration, and adaptation, you will enhance your applications and delight your users.
If you have any further questions or need specific clarifications, feel free to ask as you embark on this exciting journey of building microservices. Happy coding!
🚀You can securely and efficiently call the OPENAI API on APIPark in just two steps:
Step 1: Deploy the APIPark AI gateway in 5 minutes.
APIPark is developed based on Golang, offering strong product performance and low development and maintenance costs. You can deploy APIPark with a single command line.
curl -sSO https://download.apipark.com/install/quick-start.sh; bash quick-start.sh
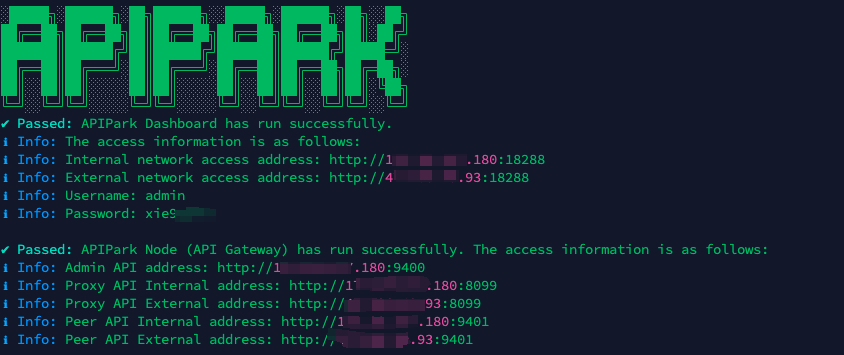
In my experience, you can see the successful deployment interface within 5 to 10 minutes. Then, you can log in to APIPark using your account.
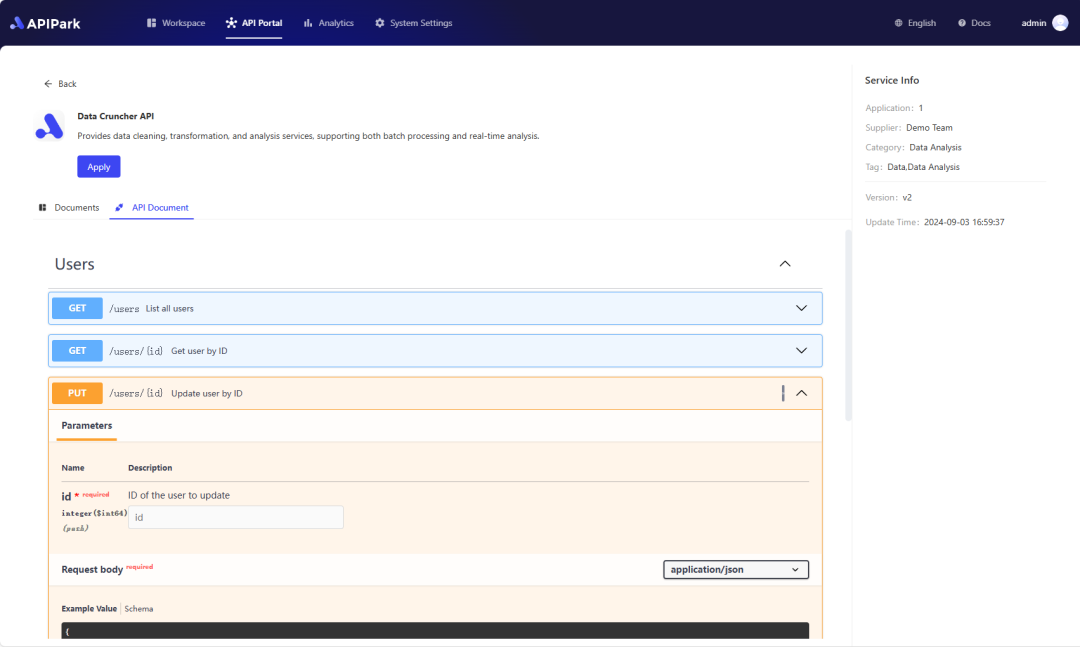
Step 2: Call the OPENAI API.