When it comes to container orchestration, Kubernetes stands out as one of the most powerful and popular platforms available today. One powerful command that is integral to local development within a Kubernetes environment is kubectl port forward. This command allows developers to forward one or more local ports to a pod. In this guide, we will explore not only the usage of kubectl port forward but also discuss its relationship with concepts like AI security, træfik, LLM Gateway open source, and Invocation Relationship Topology.
What is kubectl port forward?
The kubectl port forward command is a Kubernetes feature that connects local ports on your machine to the ports of a running pod in a Kubernetes cluster. This is particularly useful for testing and debugging applications that are running inside a Kubernetes environment without exposing them through a service.
How Does It Work?
When you execute a kubectl port forward command, Kubernetes sets up a proxy that listens on a specified local port and forwards all traffic received on that port to a pod. This allows you to interact with applications running in Kubernetes as if they were running locally.
Sample Command
Here’s how you can use the kubectl port forward command:
kubectl port-forward pod/my-pod 8080:80
In this example, local port 8080 is mapped to port 80 of my-pod. Once this command is executed, accessing http://localhost:8080 from your web browser will redirect you to the application running inside my-pod.
Why Use kubectl port forward?
The kubectl port forward command is incredibly useful for several reasons:
-
Ease of Access: You can access your applications without setting up Ingress or LoadBalancer options.
-
Rapid Development: It enables more efficient local development workflows, allowing developers to iterate quickly.
-
Testing: Facilitates the testing of your application in a real environment without exposing it unnecessarily.
Prerequisites
Before diving deeper into kubectl port forward, there are some prerequisites to keep in mind:
-
Kubernetes Cluster: You should have access to a running Kubernetes cluster.
-
Kubectl Installed: Ensure that
kubectlis installed and configured to interact with your cluster. -
Pod Running: There must be at least one pod running in your namespace to forward ports.
Understanding the Invocation Relationship Topology
When working with applications deployed on Kubernetes, it’s essential to understand Invocation Relationship Topology. This concept refers to the way different components of your application interact with one another.
For instance, if you have multiple microservices within your Kubernetes cluster, you’ll want to know which components communicate with each other, and how that communication occurs. kubectl port forward can help simulate and debug these interactions by providing access to specific services.
Table: Invocation Relationship Topology Example
| Component | Type | Ports Exposed | Dependencies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frontend Pod | Web Application | 80 | Backend API Pod |
| Backend API Pod | REST Service | 8080 | Database Pod |
| Database Pod | SQL Database | 5432 | – |
This table demonstrates the different components and their dependencies within a Kubernetes environment, giving insight into how kubectl port forward could be utilized for various service interactions.
Using kubectl port forward with AI Applications
In recent contexts, we have seen an increase in the deployment of AI applications, especially around AI security. When developing AI models or services, secure and efficient methods of testing are paramount. The kubectl port forward command can help streamline the development and testing of AI models hosted within Kubernetes.
For example, if applications use the træfik ingress controller for routing traffic, developers can leverage kubectl port forward to easily access their AI services without exposing them via a public URL. This ensures that sensitive and experimental AI functions remain secure while still being accessible locally.
Setting Up with træfik Ingress
If you are using træfik, a popular open-source ingress controller, the integration with kubectl port forward can provide seamless access to your services.
How to Enable træfik
First, ensure that you have træfik set up in your Kubernetes cluster. The basic installation can be done via Helm or YAML manifests. Once installed, your services can be accessed through the træfik ingress routes.
Example of Using kubectl port forward with træfik
kubectl port-forward svc/traefik 8080:80
This command will expose the træfik service on port 8080, enabling you to access your ingress routes locally.
AI Service Configuration
When developing AI services, it is critical to ensure that configurations support scalability and security. Using tools like LLM Gateway (a lightweight open-source gateway for language models) allows for interaction with AI services hosted in Kubernetes.
Example Configuration
For setting up a basic AI pod with kubectl, you can deploy an LLM service in your Kubernetes cluster, linking it to your application through kubectl port forward. Here’s a code snippet for a basic deployment:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: llm-service
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: llm
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: llm
spec:
containers:
- name: llm-container
image: llm/gateway:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
Once the above deployment is applied, you can forward the port and access your LLM service as follows:
kubectl port-forward deployment/llm-service 8081:8080
After executing the port-forward command, you can interact with the LLM service at http://localhost:8081.
APIPark is a high-performance AI gateway that allows you to securely access the most comprehensive LLM APIs globally on the APIPark platform, including OpenAI, Anthropic, Mistral, Llama2, Google Gemini, and more.Try APIPark now! 👇👇👇
Conclusion
In summary, kubectl port forward is an essential tool for local development in a Kubernetes environment. It provides developers with the ability to quickly access applications running within the cluster, facilitating efficient debugging and testing.
Whether you are working with intricate AI services, leveraging træfik for routing, or exploring complex Invocation Relationship Topology, understanding this command is critical. The ability to seamlessly test and develop applications while maintaining security, particularly in the rapid development of AI-integrated services, showcases the versatility and power of Kubernetes in modern tech environments.
Key Takeaways
kubectl port forwardis vital for accessing services running in Kubernetes locally.- It allows direct interaction without requiring a public route, maintaining security.
- Integration with tools like
træfikand services like LLM Gateway enhances development workflows. - Understanding your application’s Invocation Relationship Topology aids in efficient troubleshooting and structuring.
Embrace the power of kubectl port forward to elevate your Kubernetes development practices today!
🚀You can securely and efficiently call the Tongyi Qianwen API on APIPark in just two steps:
Step 1: Deploy the APIPark AI gateway in 5 minutes.
APIPark is developed based on Golang, offering strong product performance and low development and maintenance costs. You can deploy APIPark with a single command line.
curl -sSO https://download.apipark.com/install/quick-start.sh; bash quick-start.sh
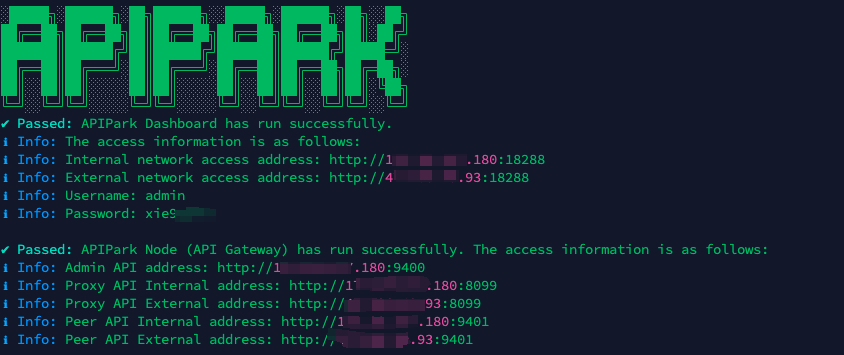
In my experience, you can see the successful deployment interface within 5 to 10 minutes. Then, you can log in to APIPark using your account.
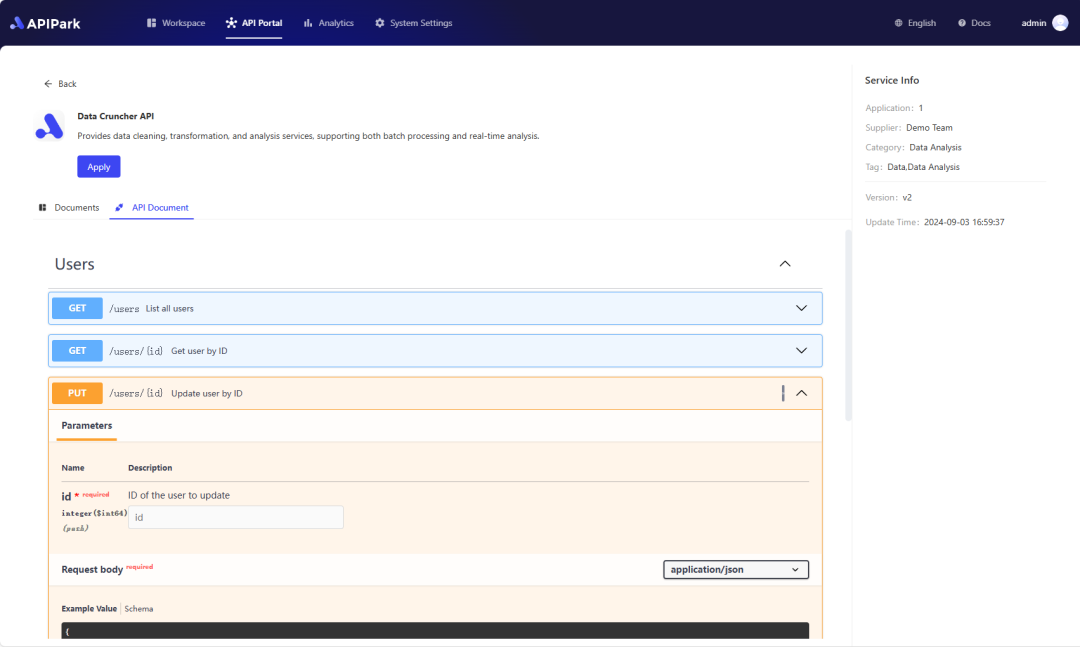
Step 2: Call the Tongyi Qianwen API.